Inventory management will shift from stocking shelves to inventory turnover ratio, average sales days and carrying costs.
Retail and restaurant industry outlook key takeaways
Retailers continue to seek ways to retain employees while investing in process improvement and automation.
Consumers will quickly pivot between different sales channels to get the biggest bang for their buck.
Middle market retailers and restaurants can enhance profitability by expanding into new markets, categories, cuisines and formats.
The retail and restaurant space faces several issues heading into the rest of 2023, including:
- Supply chain disruptions that affect product availability, quality and cost.
- Labor shortages impacting staffing, service and operations.
- Shifting consumer preferences that continue to affect demand, loyalty and profitability.
- Inflation challenges that have eroded consumer purchasing power and squeezed profit margins, requiring careful pricing strategies to balance revenue and costs.
The challenges of inventory management and price hikes in 2023
Retailers took advantage of an efficient and normalized supply chain in the second half of last year to fill once empty shelves, as retail inventories, excluding motor vehicles and parts, rose to $542.4 billion to start the year, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. The RSM US Supply Chain Index, which considers delivery time, freight traffic, job vacancy rate, manufacturing prices paid and inventory, showed a 0.5 standard deviation from neutral for January, the sixth straight month the index was positive. This disinflationary tailwind of an efficient supply chain will benefit retailers as they look for margin support in 2023.
RSM US Supply Chain Index
Z-score based on mean and standard deviation from 2001 to 2019
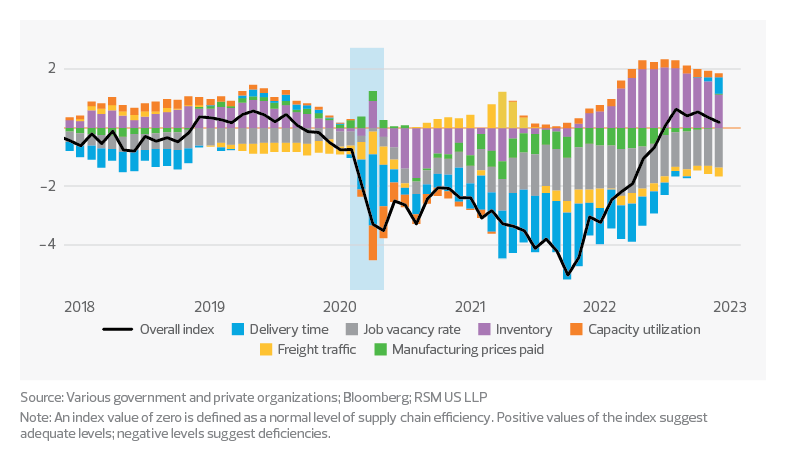
In 2023, inventory management will shift from stocking shelves to managing inventory, focusing on inventory turnover ratio, average days to sell inventory, and carrying costs. Organizations should prioritize a limited number of metrics based on company goals and anticipated customer expectations for 2023 as they manage inventory levels that could reach multi-year highs.
TAX TREND: Inventory
Elevated inventory levels and decreased demand for goods amount to an opportunity for retailers to review their inventory accounting methods—which affect net earnings and the associated tax obligations. Companies should confirm their methods align with how their inventory is purchased, how they incur direct and indirect costs, and how quickly it is turning over.
Retail workers in high demand amid labor shortages and challenges
The retail industry has continued to see labor struggles as “quits” remain elevated at a three-month average of 609.7 thousand in January 2023, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. This average is well above the 556.7 thousand in January 2020, just months before we entered the pandemic, which saw the three-month quit rate hit a high of 710.7 thousand in both December 2021 and February 2022.
Retail labor*
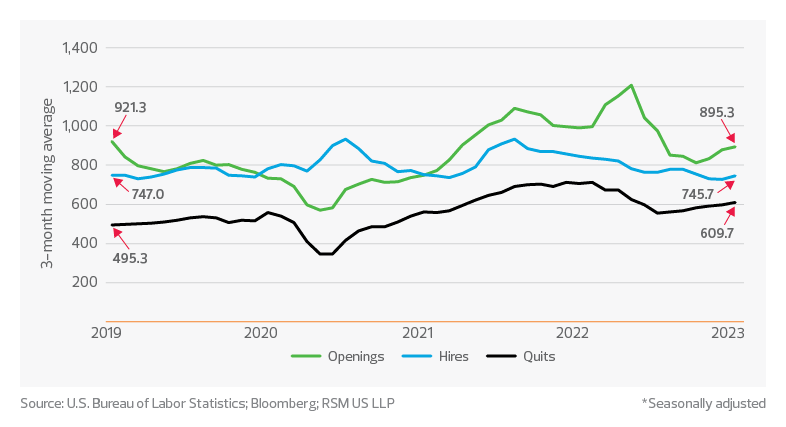
While retailers have increased the number of job openings to offset the increase in quits, hiring has remained lower at a three-month average of 745.7 thousand for January 2023 compared to the pre-pandemic level of 782.7 thousand for January 2020. Retailers continue seeking ways to retain their employees while investing in process improvement and automation to make up for employee turnover.
TAX TREND: Workforce
Developing a compensation philosophy centered on total rewards instead of just cash salary may help retail and restaurant companies balance costs with offerings that match workers’ preferences. Retirement programs, equity compensation, education opportunities or assistance and subsidized transportation benefits are just a few of many common offerings with tax implications.
Customers demand online shopping, delivery, sustainability, personalization and more
Consumers have shown a willingness and ability to adjust quickly between sales channels over the last year to fight inflation. CoreSight Research noted that nonfood store traffic increased by 14.1% year-over-year for January 2023. The increase in foot traffic also corresponded with a post-holiday bounce of 3% month-over-month in adjusted retail sales for January.
Companies in the middle market may struggle with a multichannel approach as they seek to staff retail locations while simultaneously creating and engaging in an online presence. In order to protect profits during this time, retailers should ensure they have systems and processes in place that focus on SKU profitability.
Store traffic
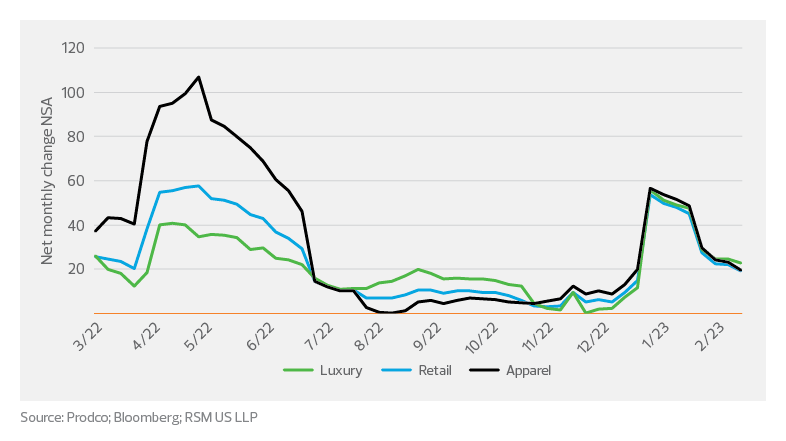
Seemingly strong consumer spending faces the sustained headwind of continued rate increases as the Federal Reserve works to temper inflation in 2023. The continued pressure will see consumers quickly pivot among a variety of sales channels to get the biggest bang for their buck. With the elevated retail inventory levels and savvy customers, companies in 2023 will need to work to ensure SKU profitability efforts return inventory ratios to pre-pandemic levels.
Middle market competitive advantages
Retailers and restaurants in the middle market segment can enhance profitability by expanding into new markets, categories, cuisines and formats. They can rely on their unique niche, local or regional appeal, loyal customer base and distinct value proposition to differentiate themselves from competitors.


