Reputational risk and costs are high if not managed proactively
Key takeaways
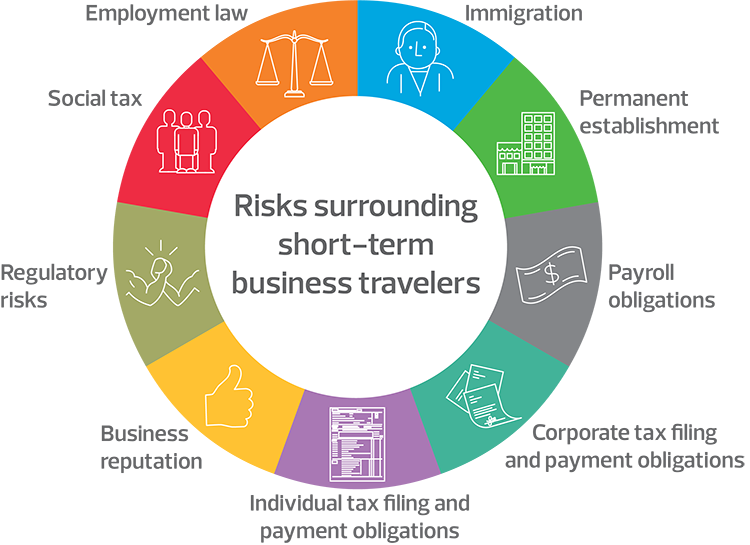
Immigration, corporate and individual tax considerations vary by country
Employees work in foreign jurisdictions while maintaining tax residency in their home country
Host countries have various tax reporting requirements and obligations which can cause significant administrative and tax burdens on the company, who may be unaware of their exposure to penalties and other regulatory risks.
RSM understands the challenges companies face tracking global business travelers and employees working remotely overseas. There is no one-size-fits-all solution. Having a foundation of key aspects to consider when sending employees overseas on short-term assignments, by country, can take considerable resources and time.
Sending employees to foreign jurisdictions
If you are sending employees to jurisdictions outside the United States, the following country-specific guides provide you, and your employees, with baseline information and insights before they arrive:
For STBTs, a single permit needs to be requested before arrival in Belgium and covers both the right to stay in Belgium and the right to work in Belgium. Learn about other important considerations for U.S. STBTs working in Belgium:
Canadian tax residency rules are not based on citizenship and are actually based on a review of the primary and secondary ties to the country. Learn more:
China resident individuals are generally subject to tax on their China-source and non-China-source income, while nonresident individuals are subject to tax on their China source income only. Learn more:
Short-term business travelers working in France should understand the definition of residency in country and ensure they are working under the appropriate visa. Other factors to consider:
To minimize the costs associated with conducting business in Germany, it is important for employers and employees to be aware of the tax implications when an employee works as an STBT in Germany. Learn more:
Ensuring travel to India is on the correct visa category is just one of many factors to consider when sending employees on short-term business assignments. Read more:
Short-term business travelers who are coming to Mexico are generally subject to tax filing and payment of income tax on their Mexico-sourced income. Read other considerations when sending employees to Mexico:
There are two ways an STBT can be considered a Swiss tax resident. One involves being in the country for 90 days with no intention to exercise a gainful activity. Find out what the second is:
Understanding the tax implications of working in the U.K. and planning travel and reporting accordingly is critical to the success of short-term assignments. Read more:
Short-term business travelers (STBTs) can trigger unexpected tax reporting obligations, for themselves and employers. STBTs are generally employees who work in another tax jurisdiction for a short period of time while maintaining tax residency in their home country. When sending employees on a short-term assignment, make sure to review the following areas: