Consistent supply and demand still means retailers face concerns over product mix, channel and preferences.
Retail and restaurant industry outlook key takeaways
Restaurants can create value by improving digital engagement and deepening understanding of customer data.
Consumers and retailers will see continued increases in costs.
As retailers continue to focus on margin in 2023, they will face the headwinds of increased cost of capital, shifting consumer spending and ongoing labor constraints. Strategic retailers will adopt multiple ways to navigate to profitability in the coming year and beyond.
Consistency does not mean profitability
While retailers will see the return of consistency in both foot traffic and number of products on the shelf, the ability to sell and move products profitably in the face of headwinds will be key. The RSM US Supply Chain Index, which provides a near real-time and forward look at transportation, manufacturing, sales and labor involved in the supply chain, was at 0.49 in October 2022, indicating that goods have resumed moving efficiently through the supply chain. Customer traffic data shows year-over-year variance in foot traffic stabilizing, with third-quarter 2022 reflecting the lowest variance for retail and luxury, at 14.3% and 17.1%, respectively.
Consistent customer traffic
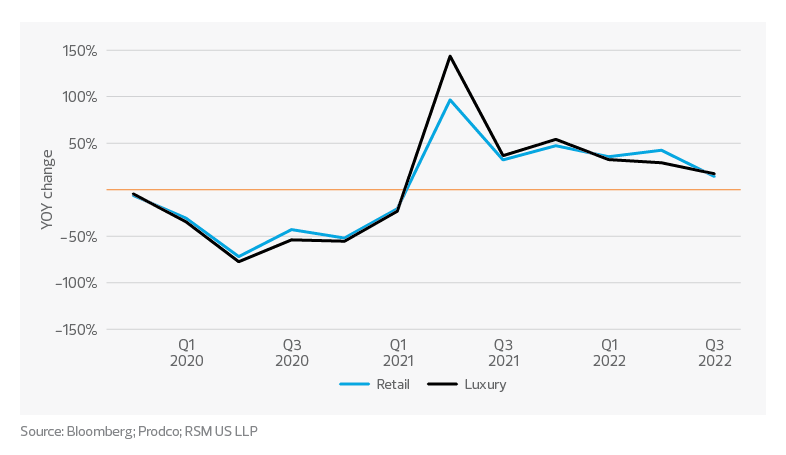
Even as supply and demand stabilize, retailers are facing new challenges because their product mix, sales channels and consumers have changed over the last three years, adding complexity to their focus on future profitability.
TAX TREND: Retail and restaurant
Elevated inventory levels and high inflation make this an opportune time for retailers to review their inventory accounting methods—which affect net earnings and the associated tax obligations. Companies should confirm their methods align with how their inventory is purchased, inventory costs and how quickly it is turning over.
Continued cost pressure for all
Both consumers and retailers face a prevailing headwind going into 2023: continued increases in costs. Consumers have seen the year-over-year price of their basket of goods rise above 4% every month since April 2021, a year after the pandemic began. The sustained headwind for households was buoyed by government spending in the form of stimulus and the child tax credit programs. The savings consumers built up during the pandemic with the support of these programs will only go so far given the budgetary pressure they continue to face. The 2022 back-to-school season highlighted how consumers were adjusting their spending patterns to stretch their budgets further. In 2023, we will see consumers at higher income levels begin to change their behaviors.
Sustained cost pressures
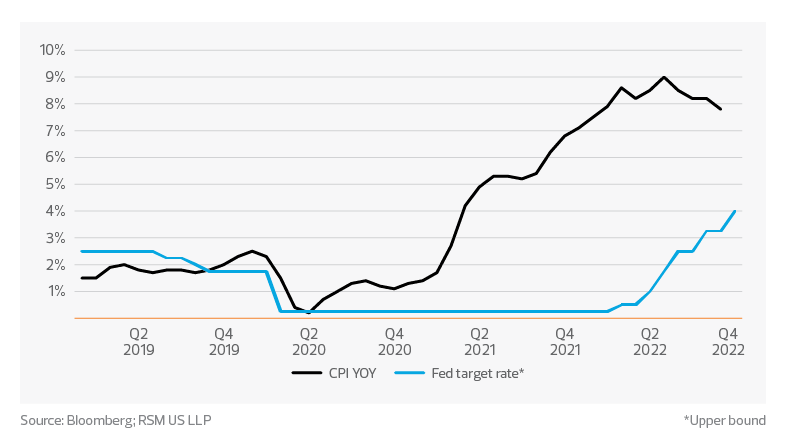
The Federal Reserve has sought to ease the pressure on the consumer by raising the federal target rate. The increased rate is going to put pressure on all retailers as they look for labor-enhancing investments in technology, future capital expenditures and customer-focused tool sets.
Experience versus food at home
Consumers looking to stretch their budget have more options when it comes to the restaurant space. Consumers are not only trading down from higher levels of service, but also trading out of the food service industry to food at home.
Returning customers
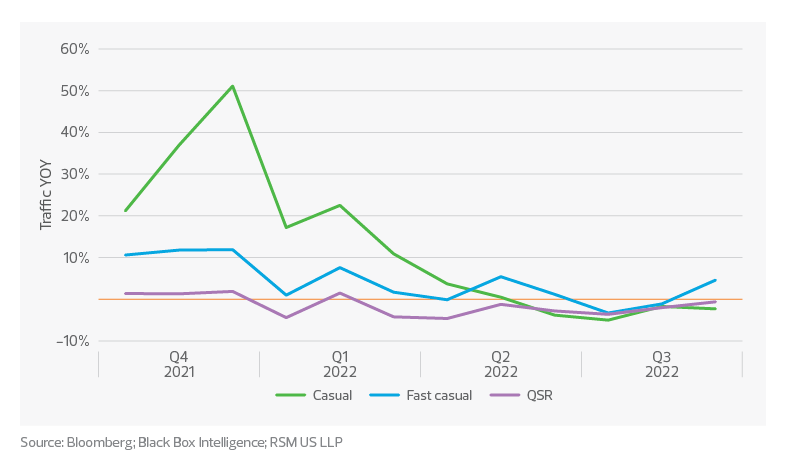
The additional pressure to attract and retain customers by engaging them beyond a single transaction is forcing restaurants to look at their entire value chain.
Restaurants are creating value for their consumers by improving digital engagement and using data to deepen their understanding of customer preferences.
TAX TREND: Retail and restaurant
Restaurants and retailers whose operations were affected in 2020 and 2021 by coronavirus mitigation measures may be eligible to claim employee retention tax credits for the covered periods, subject to eligibility requirements. Many companies did not have the resources to garner this credit, but there still is time to make sure your business is not leaving money on the table.


