The FDA and MITRE released an updated playbook focused on preparedness and collaboration against cyberthreats.
Key takeaways
Medtech device growth is being led by the in vitro diagnostics, cardiology and surgical device segments.
Despite market volatility and Fed rate fluctuations, medtech has demonstrated resilient growth over the past two decades.
New FDA regulatory guideline announcements
The digital revolution has transformed the medical technology sector, leading to the development and adoption of cutting-edge medical devices that have significantly improved patient care. However, these advancements have also exposed the sector to an array of cybersecurity threats that can potentially compromise patient safety and device functionality.
Recognizing the need for robust security measures, the Food and Drug Administration, in collaboration with the MITRE Corporation—a not-for-profit organization that manages federally funded research and development centers—released an updated version of the Medical Device Cybersecurity Regional Incident Preparedness and Response Playbook on Nov. 15, 2022. This comprehensive resource aims to equip health care delivery organizations, medtech companies and other stakeholders with the necessary tools to effectively prepare for and respond to cybersecurity incidents.
Highlights of the playbook include:
- Incident preparedness: A framework for creating customized and timely incident response plans includes identification of key roles and communication protocols, as well as an inventory of medical devices.
- Risk assessment and management: The guidance stresses regular risk assessments, vulnerability analysis and implementation of mitigation strategies.
- Collaboration and information sharing: Cooperation among health care organizations, manufacturers and stakeholders is encouraged to strengthen the sector's cybersecurity position.
- Incident response and recovery: A step-by-step approach aims to minimize the impact of cybersecurity incidents on patient safety, device functionality and organizational reputation.
- Training and education: Health care personnel need ongoing training and education to ensure they are well equipped to identify, respond to and recover from cybersecurity incidents.
- Continuous improvement: Incident response plans should be updated regularly to stay ahead of emerging threats and enhance overall cybersecurity resilience.
Looking forward, by adopting these best practices and fostering a culture of collaboration and information sharing, medtech and health care organizations can strengthen their cybersecurity position, protect patient safety, and maintain the functionality and integrity of medical devices in an increasingly interconnected and vulnerable digital landscape.
As the rate of technological innovation accelerates, continuous evaluation and improvement of cybersecurity measures will become even more crucial. By staying ahead of emerging threats and working together across sectors, these organizations can create a resilient ecosystem that safeguards both patient data and the critical medical infrastructure upon which lives depend.
Market outlook for the top 3 device segments
The global medtech sector has grown significantly in recent years, reaching total sales of approximately $533 billion in 2022, according to data from Evaluate. Among the top three segments in terms of sales are in vitro diagnostics, cardiology and surgical devices. These categories alone made up over $180 billion of sales and are predicted to grow to over $220 billion by 2027. This growth can be attributed to several factors, including technological advancements, an aging global population, increased prevalence of chronic diseases, and a growing emphasis on preventive care and personalized medicine.
Device sales by segment
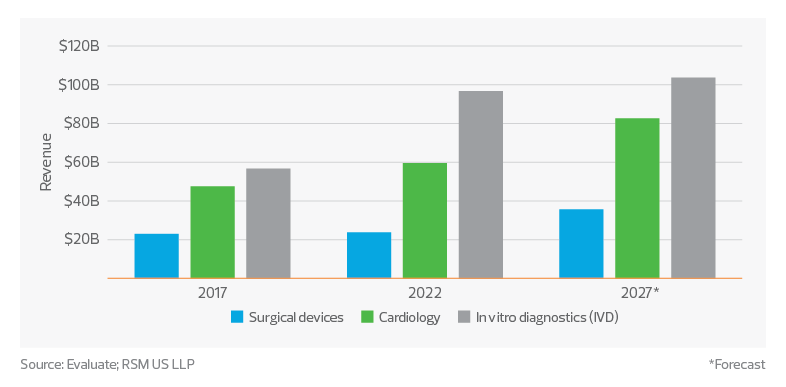
In vitro diagnostics
The ongoing development of molecular diagnostics, point-of-care testing and next-generation sequencing technologies has greatly improved the sensitivity, accuracy and speed of diagnostic tests, leading to earlier disease detection and more personalized treatment plans. The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the importance of rapid and accurate diagnostic testing, driving demand for IVD products in both infectious disease testing and areas such as oncology, genetic testing and autoimmune disorders.
The growth in this segment is also fueled by a shift toward preventive care and personalized medicine as health care providers and patients increasingly recognize the value of early detection and targeted therapies. This trend is expected to continue to drive the development of new IVD tests and expand the overall market for these devices.
Cardiology
The prevalence of cardiovascular diseases continues to rise globally, driven by an aging population and increased rates of obesity, diabetes and hypertension. This has led to a surge in demand for advanced cardiovascular devices such as pacemakers, defibrillators and heart valves.
Technological advancements in this segment are also propelling growth. For instance, the development of minimally invasive procedures, such as transcatheter aortic valve implantation and percutaneous coronary intervention, has revolutionized the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Additionally, advances in cardiac monitoring, wearable devices and telemedicine have enabled better disease management and remote patient monitoring, further driving the demand for cardiology devices in the coming years.
Surgical devices
Strong growth is also forecast for the surgical devices segment over the next five years, fueled by innovations in minimally invasive and robotic surgery. These technologies have led to reduced recovery times, less pain, and fewer complications for patients, driving increased adoption of these procedures.
One key technological improvement driving growth is the advancement in robotic surgical systems, which provide enhanced precision and control for surgeons, leading to better patient outcomes. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in surgical devices is expected to improve surgical planning, decision-making and real-time intraoperative guidance.
Demand for these devices is also being driven by a growing consumer preference for minimally invasive procedures as well as by the increased adoption of surgical procedures in emerging markets due to improving health care infrastructure and rising disposable incomes.
TAX TREND: Research and development
Many medtech companies are facing increased cash and compliance costs resulting from the unfavorable change to the required tax treatment of R&D expenses. The inability to immediately deduct these expenses from taxable income may mitigate the value of certain tax attributes that were previously thought to be favorable. Companies expanding into new jurisdictions or entering into third-party collaboration deals can minimize unexpected costs by understanding how this new requirement affects their tax obligations.
Companies might minimize this burden by analyzing their R&D expenses to ensure proper treatment and carve out those that may not require capitalization under the new law. And once a company identifies and quantifies its R&D expenses, it may find it is eligible for an R&D tax credit or other incentives.
Long-term medtech performance remains resilient, driven by innovation and consumer demand
Over the last two decades, the S&P Health Care Equipment Index and the Federal Reserve rate have experienced significant cycles and changes in performance. We can divide this 20-year period into five distinct time periods, each characterized by unique market conditions and economic factors.
Medtech market performance*
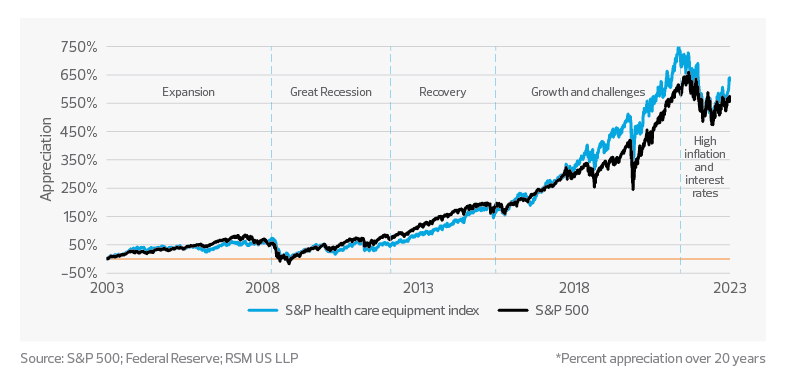
2003−07: Economic expansion and medtech growth
The U.S. economy experienced a period of growth following the early-2000s recession. The Fed rate was lowered to stimulate economic growth, which led to increased lending and spending. The S&P Health Care Equipment Index benefited from the overall economic expansion, as well as rapid advancements in medical technology, including the emergence of minimally invasive procedures and the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic devices.
2008−12: The Great Recession and market volatility
The 2008−09 financial crisis led to a sharp increase in market volatility, with the S&P Health Care Equipment Index experiencing significant declines. The Fed responded by lowering interest rates to near-zero levels in an attempt to stabilize the economy and encourage lending. Despite the economic downturn, the medtech sector remained relatively resilient due to its essential role in health care and continued innovation.
2013−16: Recovery and steady growth
This period saw a gradual recovery of the U.S. economy, with the Fed slowly raising interest rates in response. The S&P Health Care Equipment Index experienced steady growth during this time, as the industry continued to innovate and benefit from an aging population, increased prevalence of chronic diseases, and a growing focus on personalized medicine. The implementation of the Affordable Care Act also expanded access to health care, boosting demand for medical devices and technologies.
2017−22: Market growth and unprecedented challenges
The years leading up to 2022 saw continued growth in the S&P Health Care Equipment Index, driven by advancements in areas such as robotic surgery, AI and digital health. However, the onset of the pandemic in 2020 led to unprecedented challenges for the global economy and the health care sector. The Fed responded by cutting interest rates to near-zero levels again in an attempt to mitigate the economic fallout. The medtech industry played a crucial role during the pandemic, with increased demand for diagnostics, personal protective equipment, and remote patient monitoring technologies.
2022 and beyond: High inflation and higher interest rates
This period presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities for the medtech sector. While it may face hurdles related to increased borrowing costs, higher production costs and currency fluctuations, the sector’s essential nature and potential for innovation could help it navigate this distinct economic environment. Companies with strong competitive advantages and essential products and services may maintain their profitability and attract investors seeking relatively safer investment opportunities.
Overall, the medtech sector has exhibited consistent growth over the last two decades, with occasional fluctuations. The Fed rate has varied, with low rates during crises to stimulate the economy. Low interest rates have led to record valuations, contributing to larger but fewer mergers and acquisitions.
TAX TREND: Mergers and acquisitions
The new required tax treatment of R&D expenses is also affecting M&A by worsening the tax posture of targets. Transaction planning that includes R&D cost analyses may help deals proceed by reducing the cash tax rate. However, the utilization of favorable tax attributes, such as net operating losses, may be limited by a change in ownership, and that must be factored.
A look forward
As economic headwinds persist, valuations may decline further, but cash-rich buyers continue to express interest. The potential for carve-outs and divestitures of strong-performing businesses remains. Nonetheless, the S&P Health Care Equipment Index demonstrates resilience, driven by innovation and demand for medtech products.

