More connectivity is possible with edge computing, bringing applications closer to data sources.
Key takeaways
Investment in 5G infrastructure has increased with demand for increased speed and reduced latency.
Speed and density with future edge computing will benefit both enterprise customers and consumers.
The modern economy has benefited immensely from the expansion of mobile connectivity and high-speed broadband technology—both of which are necessary to support edge computing. IBM has defined edge computing as “a distributed computing framework that brings enterprise applications closer to data sources such as IoT devices or local edge servers.” The company adds, “This proximity to data at its source can deliver strong business benefits, including faster insights, improved response times and better bandwidth availability.”
Full ecosystems have been built around mobile connectivity, including transportation network companies, on-demand delivery and curbside pickup. Many more traditional ecosystems are becoming dependent on mobile connectivity as well. We’ve all been to a restaurant without physical paper menus, while some restaurants no longer employ servers in a traditional capacity and patrons must place orders via a QR code. Airlines, sporting events, and concerts have been moving to mobile boarding passes and tickets for years. All these experiences were made possible by advancements in mobile telecommunications technology and software programming.
Looking forward, a transition is taking place as faster, more dispersed, and more capable connectivity technologies are deployed in a hyperconnected Internet of Things era, in which every piece of technology in our physical world may potentially have compute and connectivity capabilities built in. This environment is becoming possible with edge computing, which is integrating everything from simple household appliances like doorbells, lights and toasters, to remote and perhaps automated surgical operations and fully automated robotic manufacturing lines.
Telecom companies of all sizes are central in building out the low Earth orbit satellite networks and broadband 5G infrastructure to support these highly complex and capable technologies. With a well-thought-out strategy, many middle market telecom companies should be positioned to capture business growth from an expanding market and newly possible products and services executed by providers and enabled by edge computing.
Increased demand for high-speed connectivity and government funding will drive increased investment
Driven by the demand for increased speed and reduced latency, investment in the infrastructure necessary to support a 5G rollout has been increasing for years, although perhaps not in a manner that provided equitable access. Investment has been turbocharged in the United States, primarily through the 2021 Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, which sets aside $65 billion to support high-speed internet connectivity. This funding targets the expansion and improved access to high-speed internet across the entire country—specifically in rural areas. The sheer amount of nonrecurring government investment, combined with private capital from the nation’s largest mobile and broadband providers, sets the stage for multiyear infrastructure spending and upgrade cycles that should benefit businesses across the entire telecom ecosystem.
TAX TREND: 5G and semiconductors
The advanced manufacturing investment tax credit and new federal grant products introduced by the CHIPS and Science Act of 2022 create substantial benefits for manufacturers in the semiconductor sector, including middle market manufacturers of the tooling and equipment used in the semiconductor manufacturing process. Proposed regulations released in March help clarify eligibility requirements.
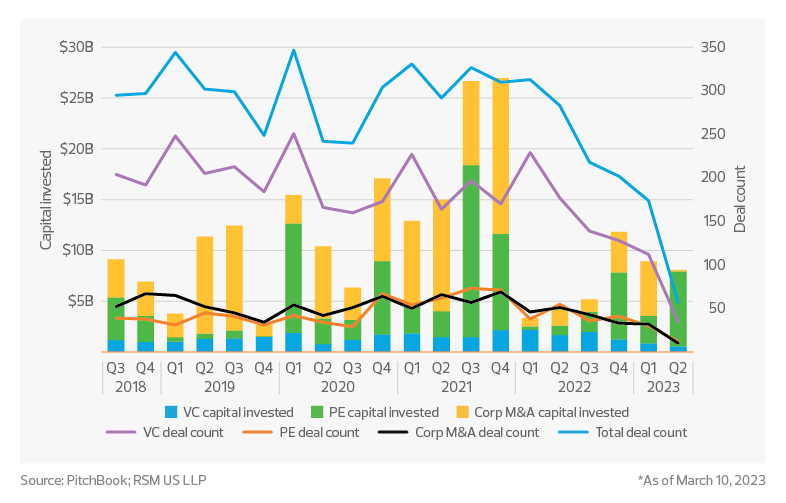
Private investment from venture capital, private equity and corporate M&A in this space has seen $219 billion of deal activity since the end of Q2 2018. That total excludes the $47 billion acquisition of Sprint by T-Mobile in Q2 2020. According to data tracked by PitchBook, nearly half of the deal activity in the communications and networking ecosystem was driven by corporate M&A, with 37% and 13% driven by private equity and venture capital, respectively.
Communications sector investment activity
The challenge: Enterprises and consumers alike will begin to demand edge computing capabilities
Enterprise demand for and creation of useful data has significantly grown in the past decade and has become more dispersed according to International Data Corp. A recent IDC report projected that 60% of all deployed network infrastructures would be edge networks in 2023, up from 10% in 2020, and cloud industry spending would reach $639 billion, growing from $328 billion in 2020. In addition, the Linux Foundation projects that cumulative capital expenditures on edge network hardware and infrastructure will reach $800 billion between 2019 and 2028. This investment will expand on what is possible when artificial intelligence, machine learning and cloud computing are combined with the ultrahigh processing speeds afforded by 5G wireless technologies.
As the availability of edge computing continues to grow, its adoption will largely be driven by the value it provides to enterprises. That is where investments will be focused in the near term, to make the implementation and use of edge computing as seamless and powerful as the deployment and use of the public cloud. In many ways, enterprises have already experienced edge computing as data center providers, and public cloud offerings have been built out to many locations. However, future edge computing will be far more local and, in some cases, done right on a connected device. In this hyperlocal model, the true benefits of low latency, speed and network density will enable new technologies or enhance those already in use, bringing value to enterprise customers as well as directly to individual consumers.
TAX TREND: Research and development
Telecommunications companies that spend significant sums on research or software development likely are affected by the unfavorable change in the required tax treatment of R&D expenses. Businesses might minimize this burden by analyzing their costs to ensure proper treatment and carve out those that may not require capitalization under the new law. Once they identify and quantify their R&D costs, they may find they are eligible for an R&D tax credit or other incentives.
Telecom is the backbone of the modern digital economy more than ever before
These advancements in technology, connectivity speeds, network density, and security capabilities necessary for 5G-supported edge computing will be constructed, deployed, and managed by current and startup telecommunications companies—and those with the strongest execution of strategic planning for the hyperconnected IoT future will benefit the most from the expanding market size and novel offerings. In recent years, data has often been referred to as the oil of the modern economy, and the IDC recently referred to edge computing and high-speed connectivity as becoming the water of our hyperconnected future—a critical resource moving forward.
Fast, reliable, secure and data-driven telecommunications companies are the foundation of our society and economy. Collectively, they represent essential infrastructure in our modern world and will become more and more important as technology is built to fully utilize and benefit from advancements in the telecom ecosystem.

